In today’s uncertain global situation and increasing regional and international threats, air security forces are poised to leverage advanced technology to enhance their modern air defense strategy.
From World War II propeller to the supersonic speed of today’s fighter fleet, military aviation has promised numerous advanced fighter jets that promise dominance.
With the rapidly evolving technological advances, the horizon of air combat is shifting again with the introduction of sixth-generation fighter planes.
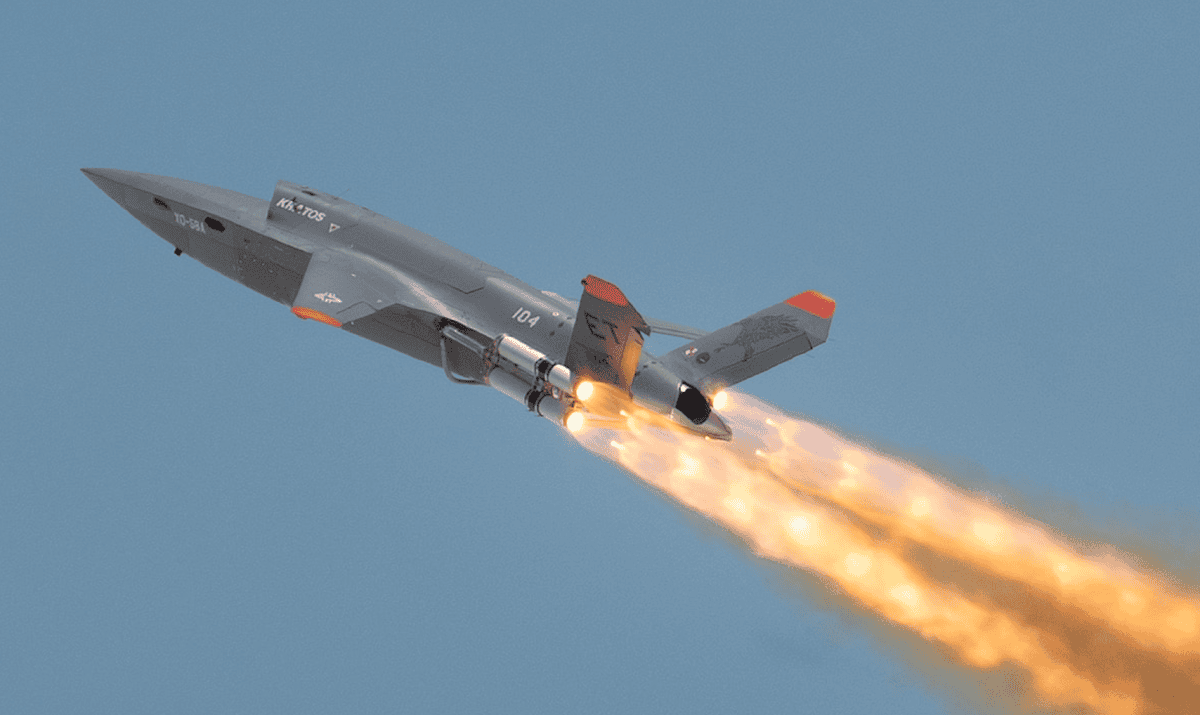
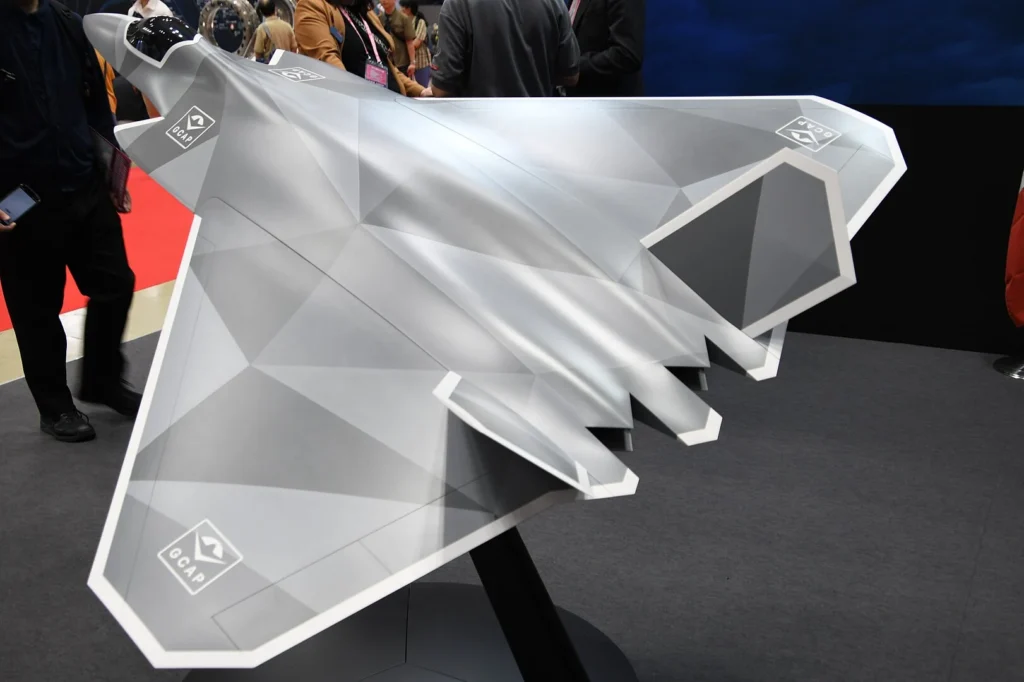 Photo: By Hunini – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=155772257
Photo: By Hunini – Own work, CC BY-SA 4.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=155772257Overview of 6th-Generation Fighter Planes
Envision jets integrated with artificial intelligence to analyze threats and coordinate in real time, engines seamlessly adapting to varied mission requirements during mid-flight, and networks where manned fighters command swarms of unmanned drones.
This is what sixth-generation fighter planes are being designed to bring superiority to air defense strategies led by the world’s leading powers.
Whether you are a fellow aerospace engineer or simply an aviation enthusiast, this post will give you important insights into sixth-generation fighter jets.
While sixth-generation fighter jets remain in development, their innovative features are already influencing future aerial dominance strategies.
Background of Previous Fighter Jets
Aviation history has introduced numerous advanced fighter jets, showcasing the evolving technical advancements. The first-generation fighter planes like Messerschmitt Me 262 and MiG-15, designed during World War II, introduced the first attempt toward piston-engined combat aircraft armed with machine guns and unguided rockets.
The introduction of semi-active radar marked the beginning of the second generation, offering supersonic speed, air-to-air missiles, and optimized interceptors.
The following generations were integrated with advanced avionics and technology like Pulse-Doppler radar, beyond-visual-range engagement, enhanced speed, and improved weapon systems to combat air-ground-air combat.
Amplified stealth, sensor fusion, high-tech avionics, and networked warfare defined the fifth generation with America’s F-22 Raptor and China’s Chengdu J-20 fighter planes.
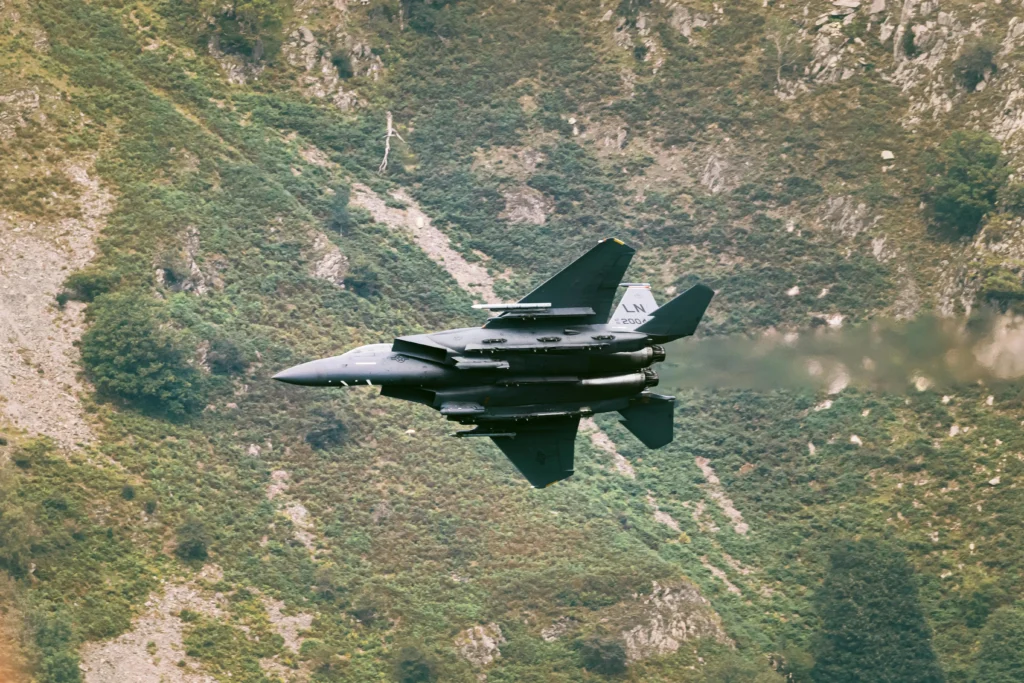 Photo: A Fifth-Generation Fighter Plane Flying Over A Valley / Pexels
Photo: A Fifth-Generation Fighter Plane Flying Over A Valley / PexelsEvolution of Sixth-Generation Fighter Planes
The world is becoming more unpredictable with each passing day. Nations are poised to develop more technically advanced air defenses, hypersonic weapons, and cyber warfare tools.
The shift from fifth to sixth generation is the next leap beyond what fifth-generation combat planes already bring.
Key Factors Driving The Need For Sixth-Generation Fighter Planes
AI is a key factor in redefining warfare systems. Today’s jets may not be enough to guarantee superiority in air defense in the decades ahead.
Estimated Development Costs
Building these advanced fighter jets is incredibly expensive. Japan’s F-X Program alone estimates a budget of $48 billion, while NGAD could cost around $300 billion when production begins.
While the potential benefits are significant, these programs also stimulate technical innovation within the aerospace sector and enhance advanced capabilities for air defense. They create high-skilled jobs and open up export opportunities.
For instance, the European stealth drone demonstrator, the Neuron program, was completed on budget and on time. Additionally, the high export sales of these fighter aircraft can generate substantial returns on investment to counterbalance the development costs.
Geopolitical Threats
Geopolitical tensions in several countries, including the Asia Pacific and Eastern Europe, are driving an arms race. Moreover, the rising military forces in Russia and China are pushing countries like the United States and European powers to pursue sixth-generation fighter planes to achieve superior air security.
Strategic Military Approach
Securing technological avionic dominance within the military is crucial in maintaining deterrence and projecting power.
These countries see sixth-generation fighter planes as the key to survival in modern conflict zones. Thus, integrating emerging technologies in new fighter plane designs becomes imperative to support aerial warfare.
Technological Innovations
The sixth-generation fighter jet concepts agree to implement some fundamental characteristics, with Artificial Intelligence being the center of it all.
The integrated AI system has the advantage of analyzing battlefield scenarios in real-time. This helps in identifying threats and even controlling autonomous drones, enabling quicker and more accurate decision-making during missions.
Several programs, including the U.S. Next Generation Air Dominance (NGAD), are already testing AI-piloted aircraft to be mission-ready with no controversies.
Networked Combat and Cloud Systems
Sixth-generation fighter planes will not fly alone. They will share real-time information with satellites, ships, drones, and ground forces.
Projects like Europe’s Future Combat Air System aim to develop next-generation air defense models by leveraging the Combat Cloud’s networked, cyber-resilient framework to strengthen real-time command, control, and communication capabilities, reducing the workload of pilots.
Enhanced Materials and Engine
The development of the sixth-gen fighter jets leverages advanced composites, such as carbon fiber, and nano-materials to build lighter airframes with improved payload capacity and energy efficiency.
This will also reduce maintenance requirements and improve durability. The aircraft’s outer body will be designed with thermal-resistant materials to suppress infrared signatures and handle the intense heat generated by hypersonic speed and energy-directed weapons.
At the same time, the adaptive engines will be able to switch between high-thrust and fuel-efficient modes depending on the missions. The optimized three-air stream engines can maximize the operational range by nearly 30%, delivering high-speed maneuvers.
Development programs like the Global Combat Air Programme (GCAP) are working with technically advanced partners to develop a new generation engine for the Tempest fighter to meet the requirements of modern air warfare.
 Photo: Chengdu J-20; fifth-generation fighter plane / Wikimedia Commons Images
Photo: Chengdu J-20; fifth-generation fighter plane / Wikimedia Commons ImagesGlobal Programs and Alliances Leading The Future
Several nations are collaborating to develop sixth-generation fighter planes to revamp their current fighter fleet and deter emerging regional and international security threats.
Unites States
The U.S. Air Force’s Next Generation Air Dominance program aims to replace the F-22 Raptor by 2030. Backed by giants like Lockheed Martin and Northrop Grumman, NGAD focuses on modular design, Artificial Intelligence, and enhanced C3 drone swarms.
Europe
A joint partnership between Dassault Aviation, Airbus Defence and Space, Indra, and Thales, Europe’s Future Combat Air System (SCAF) envisions the Next Generation Fighter (NGF) surrounded by drones, linked with an advanced Combat Cloud system for real-time data sharing. The entry into service is expected by 2040.
UK, Italy, Japan
Evolved from the British-led Tempest project, the Global Combat Air Programme (GCAP) brings BAE Systems, Rolls-Royce, Leonardo, and Mitsubishi together to design and develop the sixth-generation fighter aircraft by 2035. Funding is shared between the nations to meet each country’s specific requirements.
China
China is keeping its details closed, but it is surely working on its sixth-generation fighter planes. The country showcased a mock-up of a new aircraft, called the “White Emperor,” at the Zhuhai Air Show. Expert analysts believe it will integrate stealth, electronic warfare, and high-tech drone capabilities.
Training For The Future
The advanced leap in technology means the pilot and crew will have to learn new skills to adapt to new technologies.
To meet these requirements, training programs are evolving toward high-fidelity simulators and more interactive virtual reality environments. This is to train pilots how to use advanced weapon systems, artificial intelligence, and innovative interfaces. At the same time, mechanics will be trained in potent maintenance of new-generation composite materials and complex electronic systems.
Nations like France are already using advanced trainer aircraft, such as Pilatus PC-21, to bridge the gap between new technologies and military manpower.
 Photo: Robert Sullivan | Flickr
Photo: Robert Sullivan | FlickrStrategic Operational Scenarios
Multi-Role Capabilities
Sixth-generation air fighter planes are designed to excel in both air-to-air and air-to-ground combat. They’ll perform precision strikes, reconnaissance, and even act as a command hub for unmanned systems.
Armed with next-generation directed-energy weapons and sensory systems, sixth-generation fighter planes dominate skies far beyond visual range in air-to-air missions. Programs like NGAD are specifically designed to counter threats from stealth adversaries, neutralizing enemy targets at a far range in mid-air.
In air-to-ground missions, aircraft like the Tempest fighter can precisely strike heavily defended ground targets with greater stealth and sheer penetration.
Integrated with sensor fusions and network-centric warfare features, these aircraft will act as the ultimate spearhead in anti-access/area denial (A2/AD) zones, which older generation jets cannot easily detect.
Political Advantages
Beyond engaging in battle, sixth-generation fighter jets act as a symbol of power. It is to demonstrate an ability to deter any threats effectively.
Additionally, their hypersonic speed covers long distances in a short span, signaling the strong political and military power of the nations. Europe’s Future Combat Air Programme, for instance, demonstrates a strategically and technologically maintained partnership between France, Germany, and Spain.
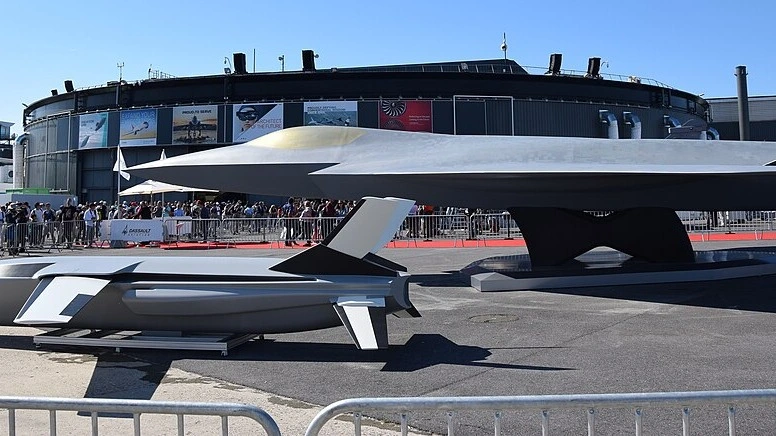 Photo: Tiraden | Wikimedia Commons
Photo: Tiraden | Wikimedia Commonshttps://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:FCAS_NGF_mock-up_at_Paris_Air_Show_2019_(1).jpg
The Future Of Aerial Defense
By the 2040s, sixth-generation fighter planes are going to shape the future of air defence systems.
These next-generation fighter planes represent the power, strategy, innovation, and ambition of the nations that possess them, playing a crucial role in deterrence.
With the advancing technology, sixth-generation fighter jets must integrate digitally enhanced air defense systems, armed drones, and cybersecurity.
From the U.S.A.’s NGAD to Europe’s FCAS and the Tempest partnership, all indicate the need for rapid development toward aerial superiority against evolving threats and the need to secure a competitive edge.
Stay tuned with us. Further, follow us on social media for the latest updates.
Join us on Telegram Group for the Latest Aviation Updates. Subsequently, follow us on Google News
Top 10 Most Dangerous Fighter Jets in the World that Never Entered Service
The post These are 6th-Generation Fighter Jets in Development in the World in 2025 appeared first on Aviation A2Z.